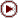
Foi
pressuposto
que
preço
de
produção R(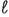 ) como
em
71b
:
) como
em
71b
:
|
R
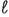 = ( K/T + k0
+ = ( K/T + k0
+ 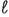 ) + (K + k0
+
) + (K + k0
+ 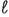 ) )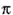 (7.1b)
(7.1b)
|
|
R
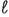 = R L
ou = R L
ou  L*
L*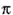 =
= 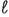 ( 1
+
( 1
+ 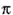 ) ) |
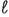 = L*
= L*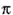 / ( 1
+ / ( 1
+ 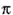 )
(7.9)
!
:184 )
(7.9)
!
:184 |
Se apesar disso, supusermos que coexistam,
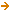 mesmo
retorno,
a
mesmo
retorno,
a 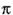 :
:O que é < > é sobreretorno e subtituição na renda vem antes: cf. Fig
  < <  L L
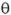 l
< l
< 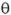 L L  Tl
< TL (vida
útil)
Tl
< TL (vida
útil) |
 Incompatibilidade em um mesmo ramo de
indústria
Incompatibilidade em um mesmo ramo de
indústria O papel temporário da forma-renda
O papel temporário da forma-renda
|
Assim, a forma-renda
e a
forma-preço são incompatíveis
em um mesmo ramo
industrial (uma mercadoria, preço).
Quando a forma-preço pode ser introduzida,
ela se generaliza e
sobrepuja a forma-renda (Ex.
histórico: Inglaterra).
|

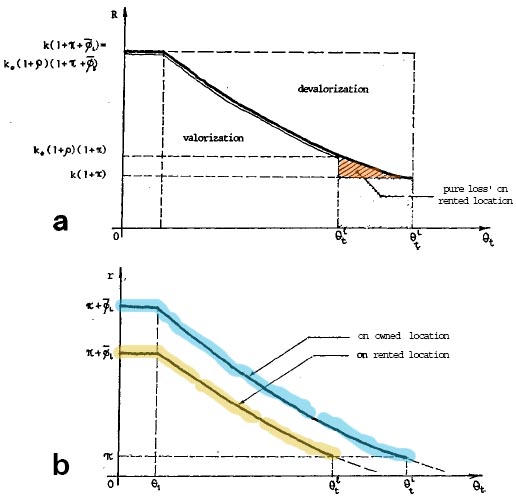
|
FIGURE
7.1: Price
form vs rent form. - If a same
technique is
employed by two processes of production on
equivalent locations, one
owning the location and the second renting it,
both processes yield the
same return R
(top) imposed by
the market price, and falling equally with the
improvement of
technique |
 Indice
TR
Espaço
Indice
TR
Espaço