| The
only essential distinction within his capital that impresses itself upon
the capitalist is that of fixed and circulating capital
Engels
in
Captal IIII: 75
|
| fixed and circulating
capital
choice of 'best technique', life time of K |
| Fall of prices > return on existing techniques |
| Obsolescence: r
falls below the avg profit rate
(assumed avg profit rate > Keynes) Substitution of old technique ("bygones are forever bygones..." Marshall) |
Bibliography.![]()
Salter,
W E G (1960) Productivity and technical change CUP, Cambridge
Deák
(1985) Chap 5: "Fixed capital and the transformation of the production
process"
(Caption
of Figure cont'd) >> in diagram (a) is
the contribution of fixed capital in total return R).
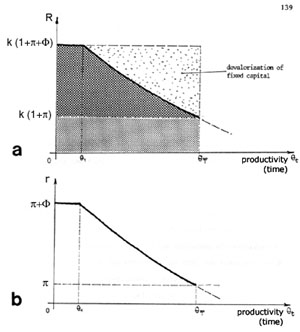
Figure 5.1- Obsolescence of the individual process of production.- As the market price falls with the increase in productivity of labour Ot, so falls the return R of an individual process of production (a, top), and consequently also the rate of return r on its circulating capital (b, bottom). When the latter falls below the assumed rate of profit p,.the technique becomes obsolete and must be substituted. At this stage, the corresponding fixed capital is wholly devalorized (darker area >